ISRO SSLV: Game changer for Low Earth Orbit

Normal 0 false false false EN-IN X-NONE PA
The Indian Space Research Organisation (AUGUST 16) successfully launched its third development flight of the small satellite launch vehicle (SSLV). The vehicle carried the 175-kilogram Earth Observation Satellite-8 (EOS-08) on board.
The EOS-08 satellite is designed to enhance environmental monitoring, facilitate the management of natural disasters, and assist with the Gaganyaan mission.
ISRO chairman: S Somanath
LEARNING FROM HOME/ WITHOUT CLASSES/BASICS
The SSLV is intended to cater to a market for the launch of small satellites into low earth orbits which has emerged in recent years due to the need for developing countries, private corporations, and universities for small satellites. The SSLV can carry satellites weighing up to 500 kg to a low earth orbit.
One can assemble the launch vehicle in less than a week. It will serve serve the growing market for small satellite launch services efficiently.
ISRO is also planning to transfer technology to private players as per the 2023 space policy.The coming of private players has poised the country’s space sector for significant expansion.
The policy recognizes the country’s need to transition from the ISRO-dominated ecosystem.
But ISRO’s role will be central to government diverse social objectives of government — education, healthcare, agriculture, climate-change mitigation, and environmental protection
SSLV
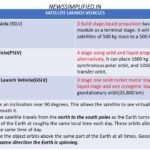
Small SatelliteSaunch Vehicle is capable of launching Mini, Micro, or Nanosatellites (10 to 500 kg mass) to a 500 km planar orbit. SSLV provides low-cost access to Space on-demand basis. It offers low turn-around time, flexibility in accommodating multiple satellites, launch-on-demand feasibility, minimal launch infrastructure requirements, etc. SSLV is configured with three solid stages. With a liquid propulsion-based Velocity Trimming Module as a terminal stage.
LAUNCH VEHICLES
The Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle, PSLV is capable of launching 1600 kg satellites in 620 km sun-synchronous polar orbit and 1050 kg satellites in geo-synchronous transfer orbit.
In the standard configuration, it measures 44.4 m tall, with a lift off weight of 295 tonnes. PSLV has four stages using solid and liquid propulsion systems alternately. The first stage is one of the largest solid propellant boosters in the world and carries 139 tonnes of propellant. The cluster of six strap-ons attaches to the first stage motor.
The Geosynchronous Satellite Launch Vehicle
Primarily developed to launch INSAT class of satellites into Geosynchronous Transfer Orbits. GSLV is a three stage launcher that uses one solid rocket motor stage, one Earth storable liquid stage and one cryogenic stage.
ISRO: It was established with its headquarter at Bangalore in 1969. It functions under overall control of department of space.
ORBITS
Different orbits serve different purposes. An orbit is a curved path of a celestial object around another celestial object due to the force of gravity. Orbits are everywhere in our universe. The Moon orbits the Earth, and the Earth orbits the Sun, and the Sun orbits around the center of the galaxy.
The near polar orbits have an inclination near 90 degrees. This allows the satellite to see virtually every part of the Earth as the Earth rotates underneath it.
Sun-Synchronous orbit; the satellite travels from the north to the south poles as the Earth turns below it. the satellite passes over the same part of the Earth at roughly the same local time each day. These orbits allows a satellite to pass over a section of the Earth at the same time of day.
These satellites orbit at an altitude between 700 to 800 km. Satellites that take pictures of the Earth would work best with bright sunlight, while satellites that measure longwave radiation would work best in complete darkness. When a satellite has a sun-synchronous orbit, it means that it has a constant sun illumination through inclination and altitude. For sun-synchronous orbits, it passes over any given point on Earth’s surface at the same local solar time.
A geosynchronous orbit is an orbit around the Earth, where the object orbits once per day. Here the object orbits above the same part of the Earth at all times. Geostationary satellites orbit in the same direction the Earth is spinning.
When the satellite is in orbit at a specific altitude, it will exactly match the rotation of the Earth. The Earth actually takes 23 hours, 56 minutes, and 4.09 seconds to make one full revolution. So this would put the satellite at approximately 35,790 km above the Earth.
It’s used for cell phone satellites, television satellites, weather satellites, as well as some military satellites.





0 Comments