India’s CAR-T Therapy for Cancer treatment launched

Recently (4th April) India’s first home-grown gene therapy for cancer, named “CAR-T cell therapy” , was launched by the President of India, Smt Droupadi Murmu; it is expected that this therapy will be available to cancer patients at a tenth of the cost abroad.
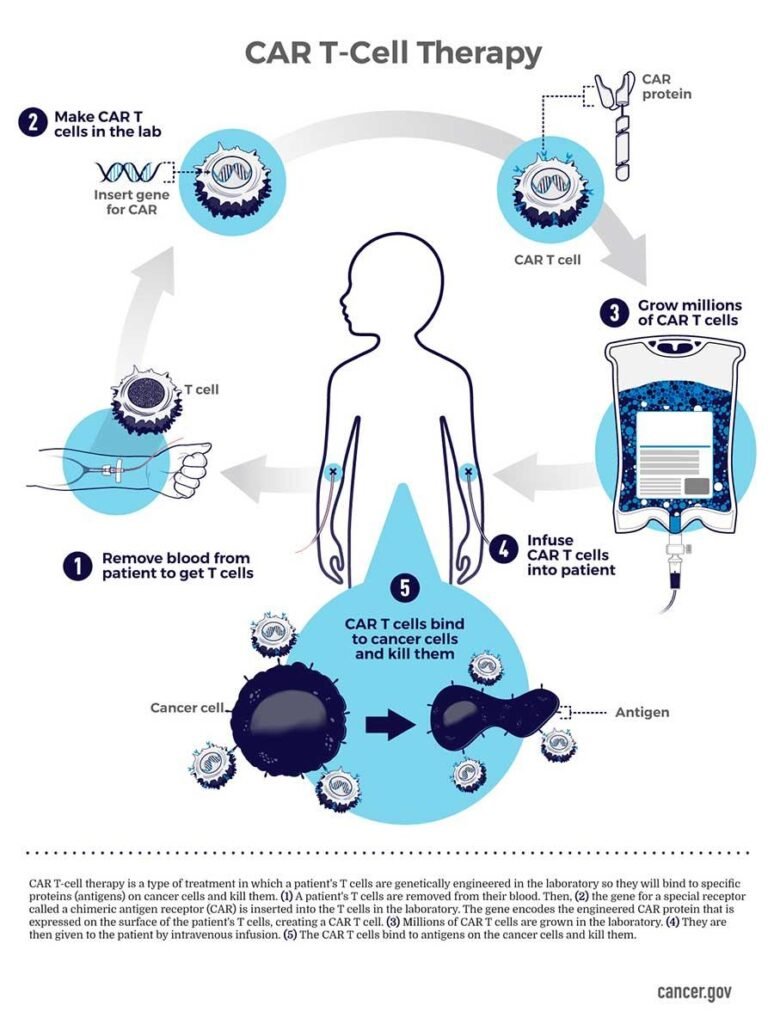
CAR-T is an innovative therapy that transforms immune cells, explicitly T-cells, by turning them into potent cancer fighters known as CAR-T cells.
T-cells, whose primary role is cytotoxic , meaning it can kill other cells, are special cells (white blood cells that find and fight illness and infection in the body).In CAR-T therapy, these T-cells are genetically modified to cancer-fighting cells. These genetically modified cells are then put back into the body, and they go after cancer cells — especially in blood cancers like leukaemia and lymphomas.
CAR-T is made by collecting T cells from the patient and re-engineering them in the laboratory to produce proteins on their surface called chimeric antigen receptors, or CARs. The CARs recognize and bind to specific proteins, or antigens, on the surface of cancer cells.






0 Comments