COP29 Agreement Falls Short: Global Disappointment Over Climate Action

The UN Climate Change Conference (COP29) meeting in Baku concluded with a slew of agreements.
In COP29 Developed countries promised to invest 300 billion dollars a year in climate finance from 2035. Developing nations demanded 1.3 trillion dollars a year.
The COP29 meeting finalized on the rules governing carbon markets. It will operationalize of carbon markets. It will allow countries to trade in carbon credits. countries agreed on standards for a centralized carbon market.
LEARNING FROM HOME/ WITHOUT CLASSES/ BASICS
COP is the annual UN Summit on the Environment and Climate Change. All the world’s leaders come together to discuss and work on climate change.
With around 1.2C of warming so far, the world has seen a cascade of climate-driven extremes in recent months, shining a spotlight on the plight of developing countries faced with escalating disasters, as well as an energy and food price crisis and ballooning debt. Scientists say limiting warming to 1.5C is a far safer guardrail against catastrophic climate impacts.
Concentrations of the main greenhouse gases – carbon dioxide, methane, and nitrous oxide – once again reached record levels in 2021. The annual increase in methane concentration was the highest on record.
ANTHROPOGENIC CLIMATE CHANGE a change caused by human activity.
CLIMATE CHANGE: Refers to any change in climate over time whether due to natural variability or of human activity.
Global warming is the long-term heating of Earth’s climate system observed since the pre-industrial period (between 1850 and 1900) due to human activities, primarily fossil fuel
burning, which increases heat-trapping greenhouse gas levels in Earth’s atmosphere.
Greenhouse gases allow sunlight (shortwave radiation) to pass through the atmosphere freely, where it is then partially absorbed by the surface of the Earth. Greenhouse gases can trap heat (longwave radiation) in the atmosphere, keeping the Earth’s surface warmer than it would be if it were not present. These gases are the fundamental cause of the greenhouse effect. Increases in the number of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere enhance the greenhouse effect which is creating global warming and consequently climate change.
Carbon dioxide (CO2); Methane (CH4); Nitrous oxide (N2O); Fluorinated gases
UNFCCC
The UNFCCC entered into force on 21 March 1994. Today, it has near-universal membership. The 197 countries that ratified the Convention called Parties to the Convention. The UNFCCC is a “Rio Convention”, one of three adopted at the “Rio Earth Summit” in 1992. Preventing “dangerous” human interference with the climate system is the ultimate aim of the UNFCCC. The ultimate objective of the Convention is to stabilize greenhouse gas concentrations “at a level that would prevent dangerous anthropogenic
(human-induced) interference with the climate system.”
PARIS AGREEMENT
The Paris Agreement is an agreement within the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC). It deals with greenhouse gas emissions, mitigation, and adaptation. The Paris Agreement signed in 2015 by 195 countries. The Agreement entered into force on 4 November 2016. The Paris Agreement mandates all countries to take action to minimize the impact of climate change. As per their voluntary commitments and individual capacity.
It sets a global goal of keeping global average temperatures from rising 2°C (compared to temperatures of pre-Industrial Revolution) by the end of the century.
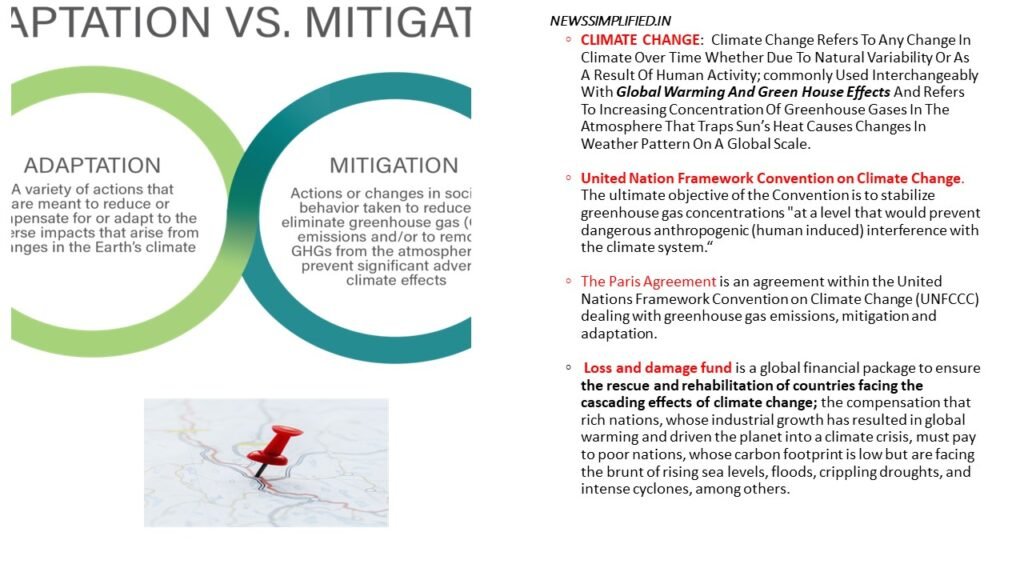
Adaptation as the process of adjusting to the current and future effects of climate change. ‘Adaptation refers to the vast range of actions societies can take to reduce the adverse impacts of global warming. Climate adaptation includes measures such as developing and rolling out new varieties of drought-resistant crops. Designing better flood-defence infrastructure to protect coastal cities or riverine communities. Improving early warning systems for climate-induced disasters, and restoring ecosystems that act as buffers against extreme weather.
Mitigation means making the impacts of climate change less severe. By preventing or reducing the emission of greenhouse gases (GHG) into the atmosphere. Mitigation measures include deploying renewable energy at scale, replacing internal combustion engine cars and motorbikes with electric vehicles, and improving the health of the planet’s forests. These can help reduce the concentration, of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere.





0 Comments